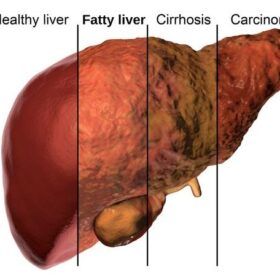
The disorder known as Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is defined by the buildup of extra fat in the liver of people who drink little or no alcohol. NAFLD, which has always been thought of as an adult illness, but it is becoming more frequently identified in children and, if ignored, causes serious health consequences.
Why this NAFLD came to our kid’s life, for that we need to understand Sugar and Diabetes.
The relationship between sugar consumption and diabetes is a topic of considerable interest and concern in the field of nutrition and public health.
Diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by elevated blood sugar levels, and the role of sugar intake.
Sugar has two parts 50% Glucose and 50% Fructose.
Glucose is a simple sugar and one of the primary sources of energy for the human body. It plays a crucial role in various physiological processes, including energy production, metabolism, and cellular function.
Fructose is a natural component of many foods, excessive consumption of fructose, particularly in the form of added sugars, has raised concerns regarding its impact on health, including its role in obesity, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome.
Unlike glucose, which is primarily metabolized in the liver and utilized by the body’s cells for energy, fructose is almost exclusively metabolized in the liver. Upon consumption, fructose is rapidly absorbed into the bloodstream and transported to the liver, where it is converted into glucose, lactate, and fatty acids through a series of biochemical reactions.
Excessive consumption of fructose can lead to the production of triglycerides and other lipids in the liver, which can contribute to the development of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), insulin resistance, and metabolic syndrome.
Fructose does not stimulate insulin secretion or leptin production, hormones that help regulate appetite and energy balance, potentially leading to increased calorie consumption and weight gain.
A balanced diet, moderate consumption of Glucose and fructose, or Sugar and regular physical activity are essential for maintaining optimal health and preventing the negative effects associated with excessive Sugar intake.
If you have concerns about your Sugar intake or its impact on your health, consult a Doctor or healthcare professional or a registered dietitian for personalized advice and guidance.
